The Medication module is integrated with the Surescripts Real-Time Formulary (RTF) solution.
- Prescribers can receive the most up-to-date plan-level formulary information at the point of care via a real-time request and response message.
- RTF data informs prescribers of a medication's formulary status, payer-provided alternatives, coverage factors, and copay details, which can assist prescribers in aligning their selected medication or treatment with the patient’s benefit plan.
Contents
Formulary Information on the Medication Sig PageFormulary Information on the Search Medication PageFAQsGlossary
Formulary Information on the Medication Sig Page
When you add or prescribe a medication, the Medication Sig page opens.
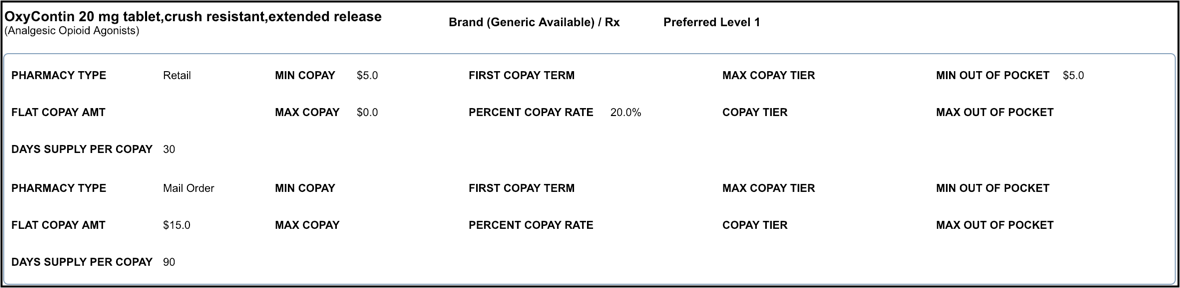
Formulary information shows at the top of the page next to the medication name. Surescripts provides additional information such as the pharmacy type and copay information. If Surescripts does not provide the information, the field or the entire section is blank.
Sample Formulary Medication
Since the medication shown below is an on-formulary, preferred medication, no alternative drugs are provided.
Sample Non-formulary Medication
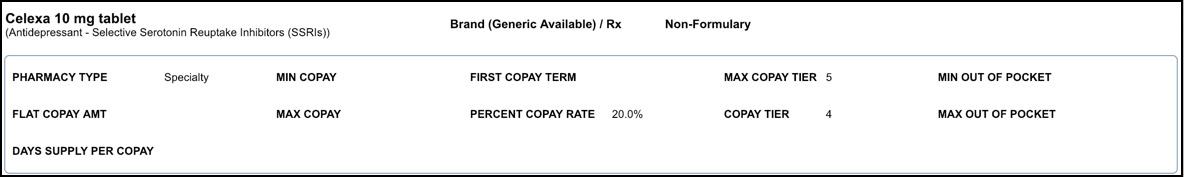
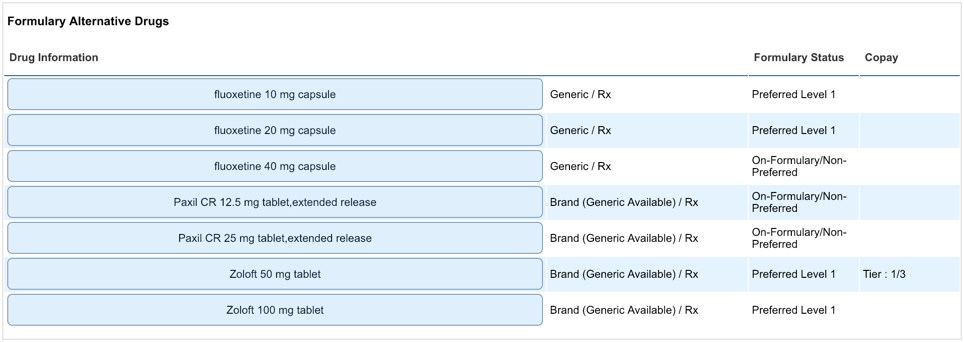
Since this medication is non-formulary, alternative drugs are presented at the bottom of the page. For more information about alternative drugs, see FAQs.
Sample Medication with Coverage Factors
Coverage factors are additional plan-level coverage details (what is covered in the patient's plan) provided by Surescripts. If there are no coverage factors, the button does not show.
- Hover over Coverage Factors.
The coverage factors window opens, which may include prior authorization, a coverage text message, and quantity limits.
- Click Close.
Formulary Information on the Search Medication Page
- Perform a medication search.
- Click Get Formulary Status.
The formulary information shows.
FAQs
When are alternative drugs provided for a medication?
Alternative medications are shown when the selected medication is:
- On Formulary/Non-Preferred
- Non-Formulary
- Non-Reimbursable
RTF returns payer-provided alternatives or therapeutic alternatives of a higher formulary status.
What is the difference between payer-provided alternatives (formulary alternative drugs) and therapeutic alternative drugs?
Payer-provided alternatives are provided by the PBM and therapeutic alternatives are derived from the EHR's drug compendia.
What is a tiered copay?
Medications are assigned to one of four, five, or six categories known as copayment or coinsurance tiers, based on drug usage, cost, and clinical effectiveness. Our prescription drug search can show you which tier applies to a specific medication based on your benefits plan. Tier 1 is the lowest tier. Low-cost preferred generic drugs are included in this tier. Tier 2 includes preferred generic drugs. Tier 3 includes preferred brand drugs and non-preferred generic drugs.
Glossary
| Term/Field Name | Definition |
|---|
| Coverage Factors | Plan-level coverage details (what is covered in the patient's plan) provided by Surescripts |
| Max Amt Qual | Maximum Amount Qualifier
Shows in the Coverage Factors window below Quantity Limits.
This field qualifies the amount in the Max Amt (maximum amount) field.
- Dollar Amount – Expressed in US currency
- Days Supply – Total number of days over which the prescription is intended to be consumed by the patient
- Fills – Total number of times that the patient obtains the prescription including the original dispensing and all subsequent dispensing under that same Rx number
- Quantity – Numeric count of the number of billing units
|
| Max Amt Time Period | Maximum Amount Time Period
Shows in the Coverage Factors window below Quantity Limits.
- Calendar Month – The time elapsed from the start of the first day of a month until the end of the last day of that same month; frequently accepted as a period beginning with a specific event on the Nth day of a month and ending at the end of the day prior to the Nth day of the next month.
- Calendar Quarter – The time elapsed from the start of the first day of a month until the end of the last day of the second month that follows; traditionally these periods start on the first day of the months of January, April, July, and October.
- Calendar Year – The time elapsed from the start of the first day of a year until the end of the last day of that same year; frequently accepted as a period beginning with a specific event on the Nth day of a year and ending at the end of the day prior to the Nth day of the next year.
- Days – Units of time composed of 24 consecutive hours.
- Lifetime – An imprecise time reference that equates to the perceived time remaining until either the end of the patient’s life or the useful duration of a product referenced.
- Per Dispensing – An imprecise time reference that equates to the perceived time between dispensing events.
- Specific Date Range – A specific period of time, as qualified by start and end dates.
|
| PBM | Pharmacy benefit manager
Third-party administrator of prescription drug programs for commercial health plans, self-insured employer plans, Medicare Part D plans, the Federal Employees Health Benefits Program, and state government employee plans. |
| Pharmacy Type | Identifies the pharmacy types returned for the requested medication that is covered for the patient. Each pharmacy type sent includes the relevant pricing, coverage alert, and prior authorization information.
- Retail: Prescription dispensed at a retail pharmacy
- Mail: Prescription dispensed via a mail order pharmacy
- 90DayAtRetail: Specifies a particular benefit supported by some PBMs designating an extended-supply prescription available at a retail pharmacy
- Specialty: Specialty medication dispensed at a specialty pharmacy
|
| Text Message | Shows in Coverage Factors. Typically provided as supplemental information to coverage alerts. |
See Also: Add MedicationsMedication SigPharmacy Benefit Eligibility


